

Įach adrenal gland has two distinct parts, each with a unique function, the outer adrenal cortex and the inner medulla, both of which produce hormones.

The adrenal glands are directly below the diaphragm, and are attached to the crura of the diaphragm by the renal fascia. A weak septum (wall) of connective tissue separates the glands from the kidneys. The adrenal glands are surrounded by a fatty capsule and lie within the renal fascia, which also surrounds the kidneys.
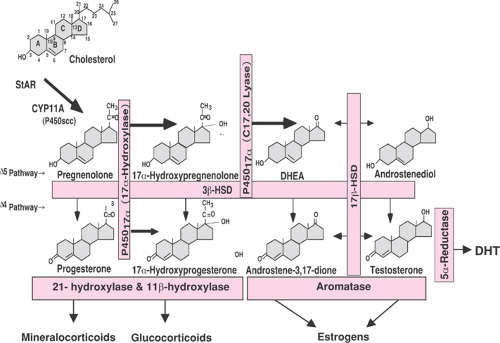
Their combined weight in an adult human ranges from 7 to 10 grams. The adrenal glands measure approximately 5 cm in length, 3 cm in width, and up to 1 cm in thickness. In humans, the right adrenal gland is pyramidal in shape, whereas the left is semilunar or crescent shaped and somewhat larger. The adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body in the retroperitoneum, above and slightly medial to the kidneys. Īdrenal glands, anterior (left) and posterior (right) surface. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Ī number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. The medulla produces the catecholamines, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
